
the  There has been a lot of talk about artificial intelligence (AI) and its impact on businesses. In this particular post, we will try to answer the most pertinent question: How has AI changed the threat landscape? This is like asking how the internet changed networking. We’ll need to narrow things down to get started.
There has been a lot of talk about artificial intelligence (AI) and its impact on businesses. In this particular post, we will try to answer the most pertinent question: How has AI changed the threat landscape? This is like asking how the internet changed networking. We’ll need to narrow things down to get started.
What is the threat landscape?
There are several distinct threat landscapes. Physical security, public health, environmental, economic, and geopolitical threat landscapes have all been affected by artificial intelligence. These landscapes overlap but have distinct areas of focus. There is also a distinction between the technology threat landscape and the cybersecurity threat landscape, as illustrated in the following table:
| Cybersecurity Threat Landscape | Technology Threat Landscape | |
| Primary Focus | Security of digital information and IT infrastructure. | Risks associated with emerging technologies across various fields. |
| Types of Threats | Malware, phishing, ransomware, data breaches, DDoS attacks. | Misuse of AI, ethical concerns of biotech, robotics safety, deepfakes. |
| Main Concerns | Data privacy, network security, information integrity. | Ethical use of technology, unintended consequences, long-term effects. |
| Affected Entities | Businesses, governments, individuals relying on digital technologies. | Wider society, including industries leveraging emerging tech, public policy domains. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Firewalls, antivirus software, security protocols, cybersecurity awareness training. | Ethical guidelines, regulatory frameworks, public awareness, research on long-term impacts. |
We’re going to stick with a cybersecurity focus for now.
What makes up the threat landscape?
Threat vectors and attack surfaces are the building blocks of the threat landscape. Threat vectors, also known as attack vectors, are the methods or mechanisms used to infiltrate a system. You could think of them as the doors and windows of a house. The house is the network, and the front door is the email threat vector where the phishing attacks could enter. Another door might be your network threat vector, where an intruder might get through a vulnerable firewall. The windows might be the web application threat vector, and so on. These are the routes for an attack to pass in or out of your system.
Using this example, we can illustrate the attack surface as the state of the doors and windows. Are they secure? Do you have more than you need? Do you know about all of them? The attack surface is the sum of all points of access and existing vulnerabilities in and out of a network or system.
Artificial intelligence has expanded both threat vectors and attack surfaces in companies and homes.
AI and cybersecurity
Machine learning and other AI capabilities have been used to reduce and defend the attack surface in every threat vector. AI-powered security will look for unnecessary services, vulnerabilities, and other gaps in security. These tools can either remediate the issue or alert IT teams to take action. AI continues to defend the remaining attack surface by monitoring the security configuration and system activity. Proactive threat hunting is part of this AI defense system. Artificial intelligence capabilities allow security systems to identify anomalies, take action, and then learn from the threat itself. It’s a powerful defense mechanism.
Here are some examples of these defenses and their effects:
| Threat Vector | AI Contribution | Effect on Attack Surface |
| Detecting phishing, spam, and sophisticated attacks | Reduced phishing & spam threats | |
| Application Security | Code analysis for vulnerabilities | Fewer software vulnerabilities |
| Network Security | Anomaly detection in network traffic | Early detection of breaches |
| API Security | Identifying abnormal API usage patterns and vulnerabilities | Reduced API-related attacks |
| Web Browser | Detecting malicious websites and phishing links | Safer browsing experiences |
| Social Media | Detecting fake news, bot accounts, and social engineering | Reduced spread of misinformation |
| IoT/ICS | Monitoring device behavior and traffic for anomalies | Enhanced security of devices |
AI and cyberattacks
Cybercrime and cybersecurity are adversarial domains. Threat actors create attacks that will challenge and learn from AI defenses. These improved attack systems can be easier, stealthier, faster, and better.
| Threat Vector | AI Contribution | Effect on Attack Surface |
| Automating the process of sending phishing emails, scanning for vulnerabilities, and responding to replies | Attacks are more scalable and efficient | |
| Application Security | Dynamically adapting to defenses in real time | DDoS and brute force attacks are more difficult to mitigate |
| Network Security | Scanning for vulnerabilities at a much faster rate than human attackers. | Faster execution of zero-day exploits and other vulnerabilities |
| API Security | Rapidly sending a variety of complex requests | APIs are overwhelmed or vulnerabilities are discovered |
| Web Browser | Matching attacks to client vulnerabilities | Custom malware is installed without human interaction |
| Social Media | Cloning profiles, collecting data on users | More identity theft and targeted scams |
| IoT/ICS | Identifying critical devices and finding vulnerabilities | New ways to infiltrate networks, larger botnets, and potential disruption of operations |
AI and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
Artificial Intelligence has significantly contributed to the growth of APIs across the worldwide threat landscape. Companies are embracing AI-powered automation, decision-making, and customer service or patient care. Much like the internet, AI will mature, and new use-cases will develop. This will lead to more APIs, more customization, and a greater attack surface for companies that do not actively manage API and application security. The threat landscape will continue to grow.
AI is the weapon of choice
Defenders and attackers are using machine learning and GenAI to protect their interests and get better at what they do. In our next post we’ll take a closer look at how threat actors are using AI to supercharge their phishing attacks.
Did you know…
According to a recent report from Barracuda and the Ponemon Institute, 50% of IT pros expect to see an increase in the number of attacks due to the use of AI. Get the details on this and a lot more in our new e-book, Securing tomorrow: A CISO’s guide to the role of AI in cybersecurity. This e-book explores security risks and exposes the vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit with the aid of AI to scale up their attacks and improve their success rates. Get your free copy of the e-book right now and see all the latest threats, data, analysis, and solutions for yourself.
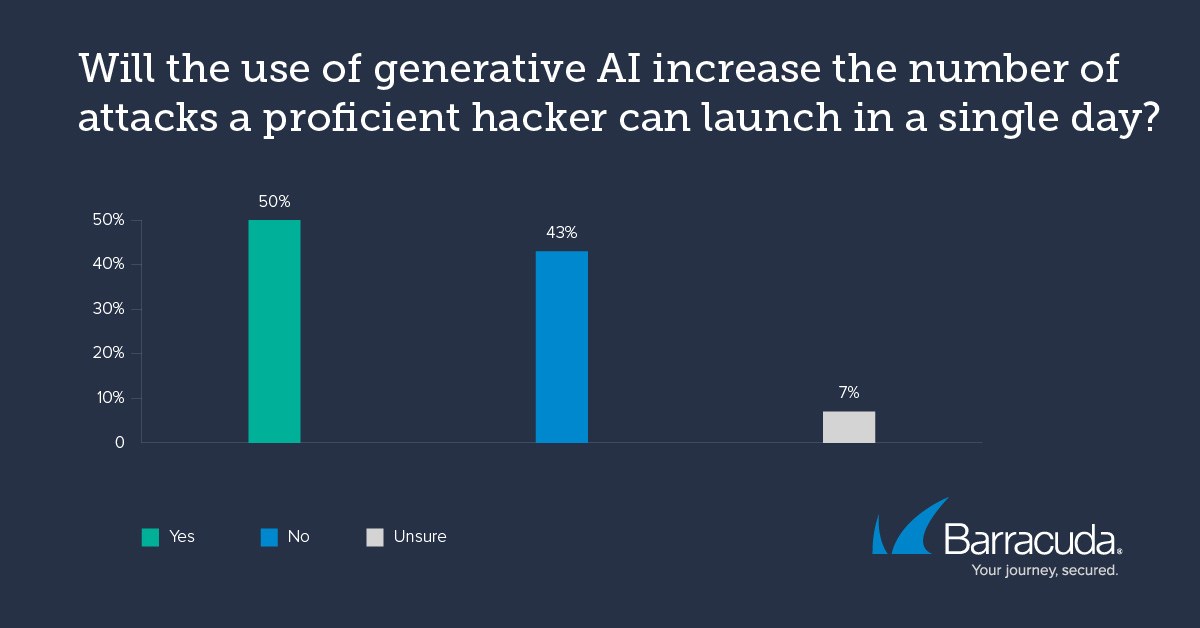
Photo: sdecoret / Shutterstock
This post originally appeared on Smarter MSP.

